Lithium metal batteries:
Lithium metal batteries generally use manganese dioxide as cathode material, lithium metal or its alloy metal as anode material, and non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
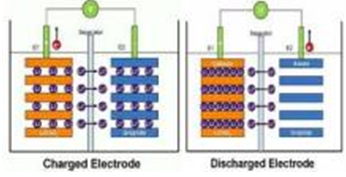
Basic principle of lithium battery
Discharge reaction: Li + MnO2 = LiMnO2
Lithium ion battery:
Lithium ion batteries generally use lithium alloy metal oxide as cathode material, graphite as anode material and non-aqueous electrolyte.
The reaction on the positive electrode of charging is
LiCoO2 = = Li (1-x) coo2 + XLI + + XE - (electron)
The reaction on the negative electrode is
6C+XLi++Xe- = LixC6
Total reaction of rechargeable battery: LiCoO2 + 6C = Li (1-x) coo2 + lixc6
Positive electrode
Cathode material: there are many optional cathode materials, and lithium iron phosphate is widely used in mainstream products. Comparison of different cathode materials:
|
LiCoO2
|
3.7 V
|
140 mAh/g
|
|
Li2Mn2O4
|
4.0 V
|
100 mAh/g
|
|
LiFePO4
|
3.3 V
|
100 mAh/g
|
|
Li2FePO4F
|
3.6 V
|
115 mAh/g
|
Positive reaction: lithium ion is embedded during discharge, and lithium ion is de embedded during charging. Charging: LiFePO4 → li1-xfepo4 + XLI + + XE - discharging: li1-xfepo4 + XLI + + XE - → LiFePO4.
Negative pole
Anode material: graphite. New research has found that titanate may be a better material.
Negative electrode reaction: Li ion is de intercalated during discharge and Li ion is intercalated during charging.
Charging: XLI + + XE - + 6C → lixc6
During discharge: lixc6 → XLI + + XE - + 6C

 Wechat QR code
Wechat QR code Mobile QR code
Mobile QR code